What do we offer?
We strengthen
The resilience of cities to floods and climate change.
We efficiently manage
Flow rates, volumes and quality of runoff with Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS).
We create
And improve the urban habitat with multifunctional spaces that promote biodiversity and recreation.
We empower
The efficient use of water resources and respect for the environment.
We add value
Using advanced hydrological-hydraulic modelling design tools.
Services
What we do?
Green Blue Management is a pioneer company in the implementation of Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) in Spain. We have been developing innovative solutions in rainwater management for almost two decades, and we have been responsible for the drafting of the first SuDS design guides published in Spain.
At GBM we provide technical assistance throughout the life cycle of SuDS, from the planning and strategy phase, to their maintenance, through all the design and project phases. We are specialists in hydrological-hydraulic modelling, using specialised and advanced software, compatible with BIM. At GBM we have designed numerous drainage systems, combining SuDS techniques with conventional systems, and in regions with very different climates.
Our main services are encompassed in three main areas:

GBM has solid knowledge to develop any type of consulting work related to the management of rainwater in urban environments and SUDS:
- Guidelines and manuals
- Feasibility studies
- Implementation strategies and planning criteria
- Master plans
- Flood risk analysis
- Scour studies
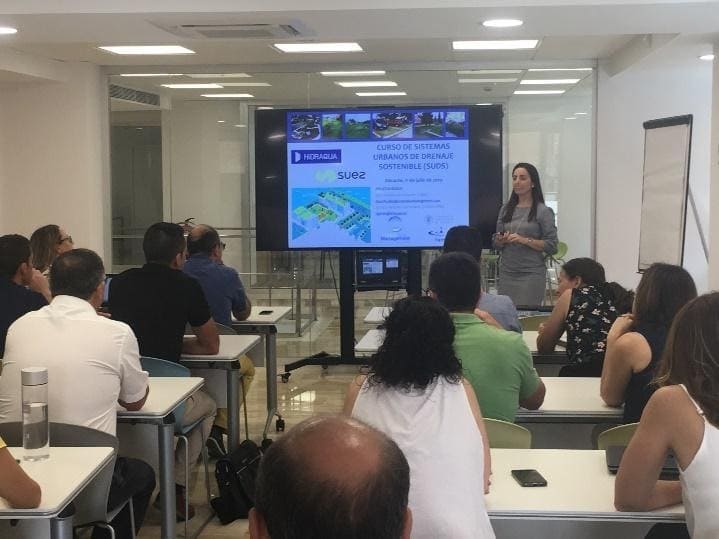
- Training, courses, conferences
- R + D + i projects
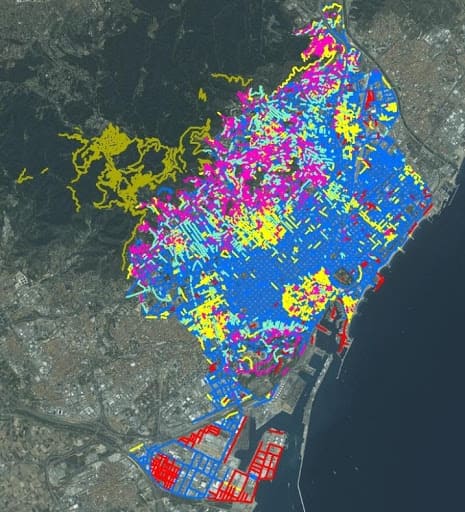
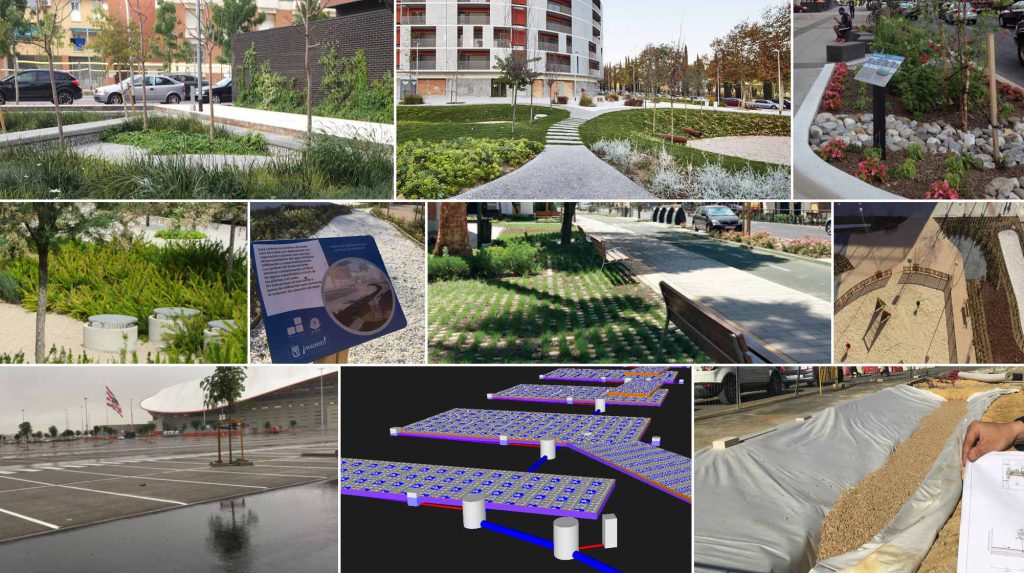
We work with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to, among other actions, extrapolate the generalised implementation of SuDS at different scales; and identify the best SuDS location to mitigate the problems of the place.
GBM carries out the design, calculation and modelling of sustainable drainage systems at different scales (street, neighborhood, city) and in different land uses (residential, industrial, commercial).
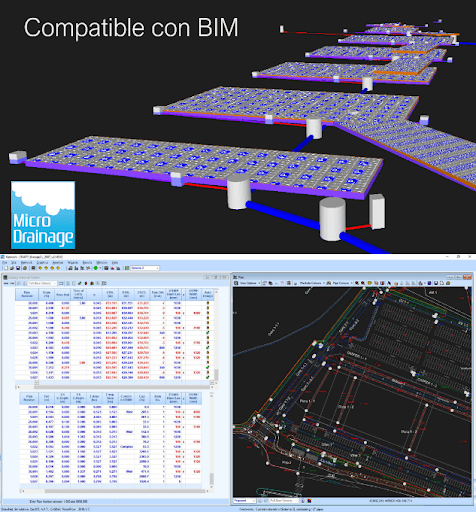
We can perform:
- Project management
- Schematic design
- Detailed design
- Constructive design
GBM has sophisticated computer tools for hydrological-hydraulic modelling, which incorporate BIM and allow the optimisation of drainage infrastructures, thereby reducing construction and maintenance costs.
We also carry out flood risk analysis studies, which are vitally important in city and infrastructure planning. Identifying potential flood areas from events of multiple sources and their effect on land uses, being able to evaluate the effect of climate change in different scenarios.
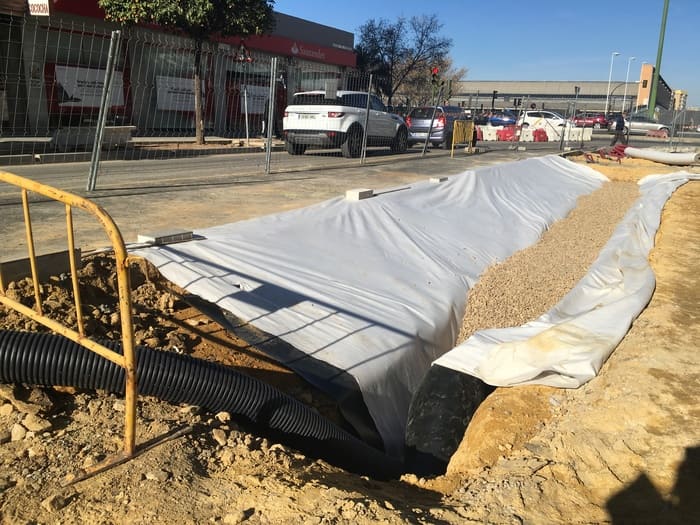

GBM services extend beyond the project phase, encompassing the following:
- Supervision of works
- Monitoring
- Maintenance scheduling
GBM advises on construction processes of sustainable drainage systems, providing support on site and guaranteeing the quality of the works.
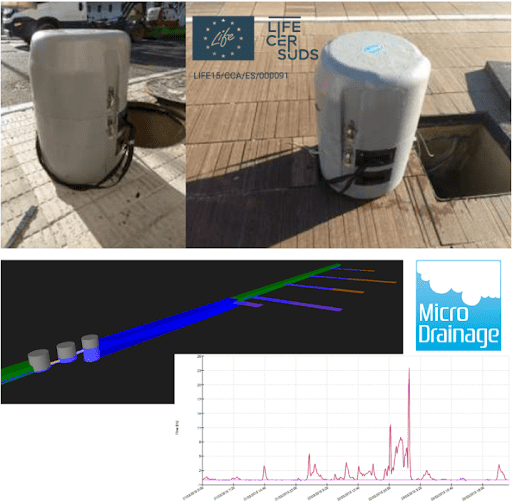
GBM develops drainage system monitoring projects, which include the selection and configuration of measurement elements. We calibrate and validate as-built models of the drainage system incorporating the data collected from the monitoring systems. The as-built model can be used to estimate of the performance of the drainage systems executed in the future events and efficiently schedule maintenance tasks, etc.
At GBM, we also develop maintenance manuals and programs to ensure the operability and aesthetics of the SuDS throughout their life cycle.
SUSTAINABLE DRAINAGE
WHAT ARE THE SUDS?
SuDS provide a TRIPLE BENEFIT by being advantageous to the economy, the environment and communities.
Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) take advantage of the properties of the soil.
SuDS are Nature-Vased Solutions (NBS) for the smart management of rainwater collecting and treating the water where the rain drops: roofs, squares, streets, roads, etc.
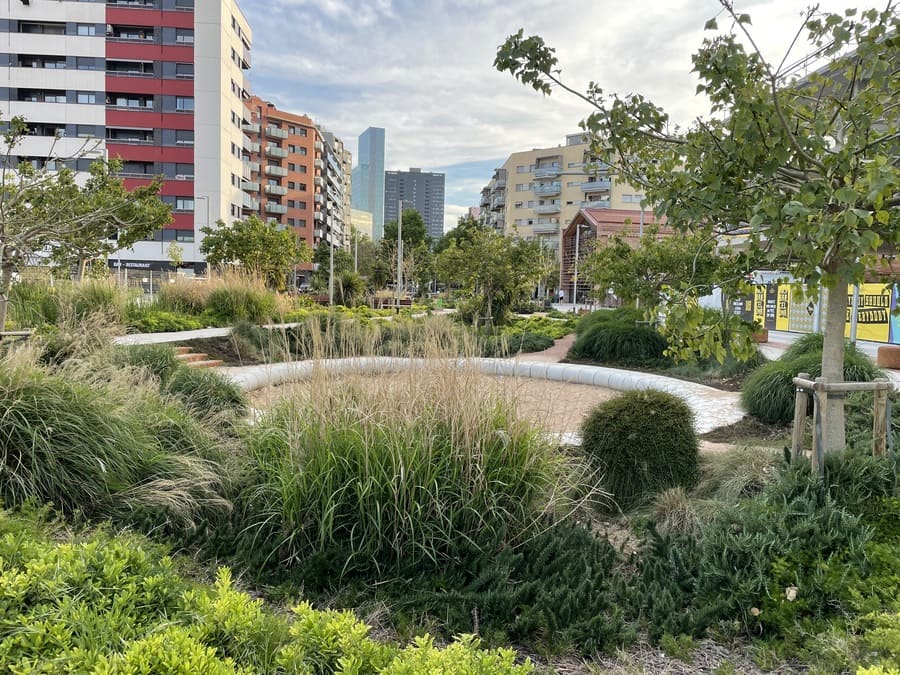
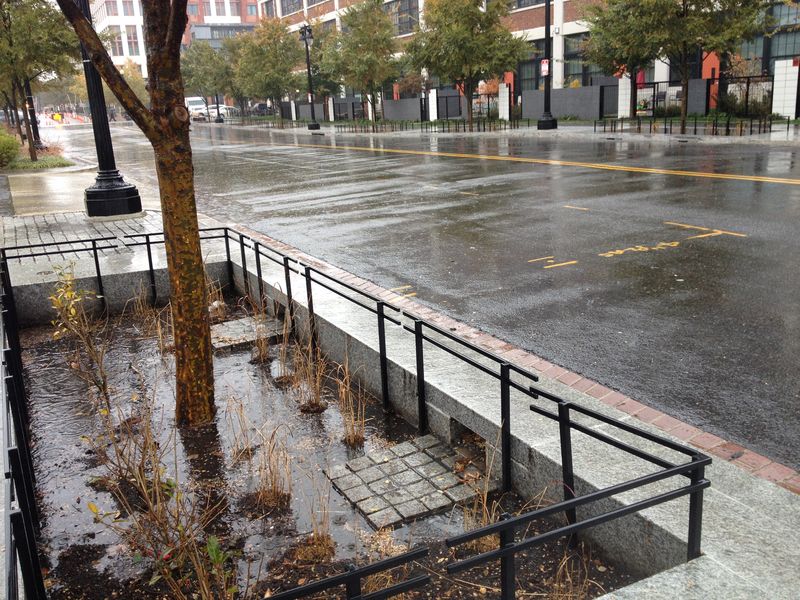



The SuDS enable a transition towards a circular economy in the city, by restoring its drainage capacity and closing the water cycle with a wide range of techniques such as rain gardens, permeable pavements, infiltration-attenuation basins, harvesting systems, among others.
SuDS substantially reduce the total amount of water discharged to sewers or watercourses.
This way, SuDS constitute a strategy for adaptation to climate change in the urban environment, by increasing the resilience of drainage systems to cope with extreme weather events, and reducing the risks from flooding and drought.
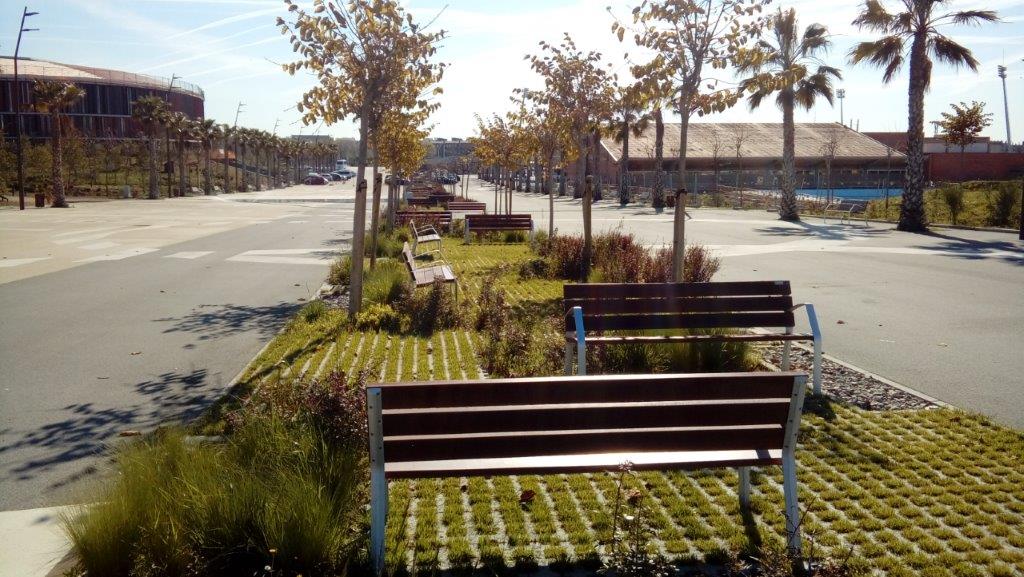

Moreover, SuDS improve the quality of the urban landscape, providing natural habitats for fauna and flora, as well as spaces for coexistence within the city. In addition, they enhance the improvement of the state of water bodies.
The sustainable drainage concept implies the increase in permeable and green surfaces, which can reduce the urban “heat island” effect that occurs in cities.
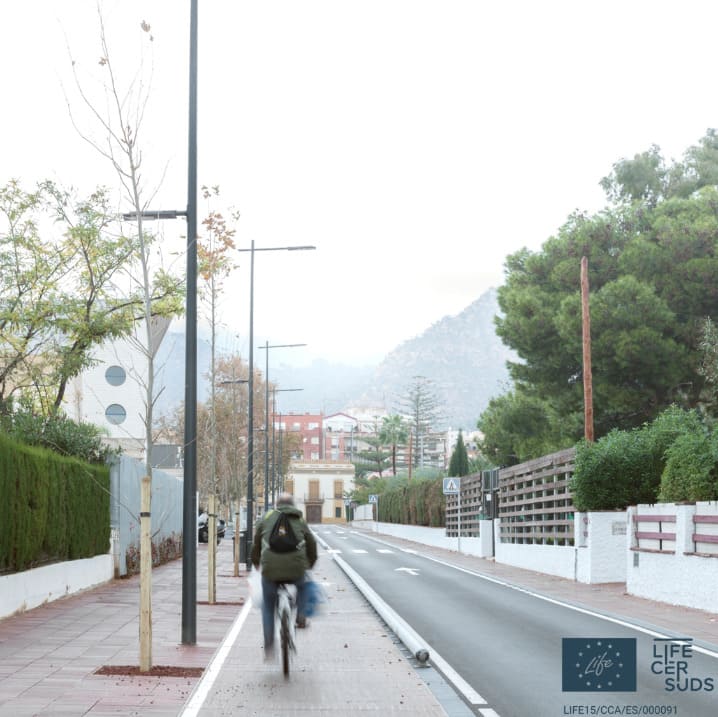


SuDS intervention can include informative boards which are a useful tool for educational and communication purposes.
THE SuDS CONTRIBUTE DIRECTLY TO THE ACHIEVEMENT OF THE SDGs

The Sustainable Development Goals are made up of 17 specific objectives of universal application that have been proposed by the United Nations to direct efforts to comply with the 2030 Agenda.
Water is a scarce good and an essential support for life and therefore several of the SDGs focus on improving the management of water resources and improving the quality of water bodies. It is at this point where the SuDS can contribute in a very important way to the achievement of these objectives by:
- Improving the quality of water bodies
- Protection against floods and droughts
- Adaptation to climate change


The green areas associated with SuDS improve the quality of the air and therefore, people’s health in general.

SuDS absorb pollutants from the water and efficiently attenuate runoff, improving the quality of water discharged into the natural environment.

In addition to improving the hydrological behaviour of cities, SuDS contribute to creating attractive urban environments and improving the energy efficiency of buildings.

SuDS help to alleviate stormwater flooding in cities and improve their resilience to climate change.

By improving the quality of the water discharged, SuDS contribute to improving underwater life and limiting nutrients discharged to the sea.

The green areas associated with the SuDS promote the creation of new habitats and ecosystems.

The SuDS require a change in urban mentality that involves several stakeholders, both public and private.

